Oil seals are used for essential applications in the oil, gas and petrochemical sectors. They are created to avoid leaks from the sealing lip and rotary shaft by forming a thin layer of oil between them. Oil seals could be developed using well-known sealing materials, involving NBR, EPDM, PolyTetraFluoroEthylene (PTFE), Silicone,and fluoroelastomer.
The oil seals represent the most important type of dynamic sealing on rotating shafts. During the last years, we witnessed a great evolution in the technology, starting from their shape to the materials used nowadays.
The functionality of oil seals in between machines cannot be emphasized. Apart from their primary function of preventing the entry and escape of elements that can damage the machines, they also help to elongate the machines’ lifespan.
If oil is dripping down your motorcycle’s tube, your vehicle’s performance will be affected. It won’t have as much power, and you’ll notice it acting sluggishly.
Free the cover by levering gently round the edge with a screwdriver; take care not to bend the flange.
Lift out the rags without dropping dirt into the engine, bores or passages.
Oil Seals Enable Your Equipment to Operate Efficiently
Other maintenance factors, such as
Stuff clean rags into the cylinder bores and all water and oil passages and bolt holes to catch scrapings and dirt.
Viton®
High level of chemical resistance
High temperature resistance
This is one of the frequent reasons for oil seal failure, and this is majorly because of the volatility of any of the elastomer’s constituents. These causative constituents may be part of the elastomer formulation, or gases that got entrapped in the elastomer during the molding process. The deceiving fact about this failure is that sometimes the oil seal won’t show any visual sign of out-gassing, however, sometimes when the out-gassing is extreme, they shrink.
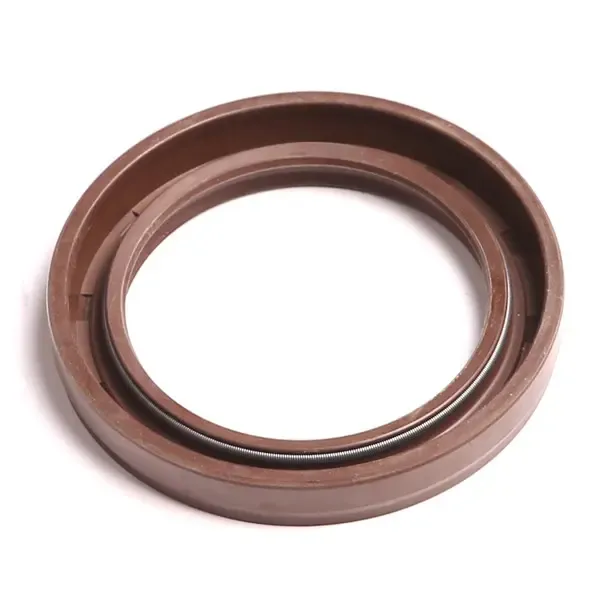

2. The most common types of oil seals are rubber-cased and metal-cased.
Fluorine rubber (FKM, Viton™)

changing spark plugs.
 In plumbing, they ensure watertight connections in pipes and fixtures In plumbing, they ensure watertight connections in pipes and fixtures
In plumbing, they ensure watertight connections in pipes and fixtures In plumbing, they ensure watertight connections in pipes and fixtures u shaped silicone gasket. In electrical applications, their non-conductivity properties make them perfect for insulating components. They even find usage in food and pharmaceutical industries due to their non-toxicity and ease of cleaning.
u shaped silicone gasket. In electrical applications, their non-conductivity properties make them perfect for insulating components. They even find usage in food and pharmaceutical industries due to their non-toxicity and ease of cleaning.5. Conclusion
Other important factors are ensuring the hardness and roughness of the shaft are correct. A shaft hardness of HRC 45 is recommended for a rubber sealing lip, with a roughness of Ra 0.4-0.8. A higher shaft hardness of HRC 60 and shaft roughness of Ra 0.1-0.4 is recommended for a PTFE lip.
 20 30 7 oil seal. They are designed to fit precisely in their designated locations, ensuring minimal friction and wear. This precision is key; a gap as small as a few thousandths of an inch can lead to disastrous consequences.
20 30 7 oil seal. They are designed to fit precisely in their designated locations, ensuring minimal friction and wear. This precision is key; a gap as small as a few thousandths of an inch can lead to disastrous consequences.Finally, consider the size and shape of the gasket, as well as any specific design requirements that may impact the gasket's performance. Custom-made natural rubber gaskets can be designed to meet the unique needs of your application, ensuring a precise fit and optimal sealing performance.

